PhD (2000-2003)
"Remote actuation of independent electrostatic Distributed Micromechanical Systems (DMMS) for a Wireless Microrobot using a micromachined antenna on a flexible substrate"
Objectives
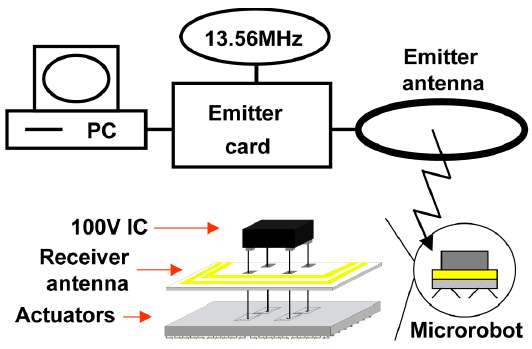
Towards the fabrication of a wireless microrobot, we realized the asynchronous remote operation of Distributed Micro Mechanical Systems (DMMS). The DMMS are made of large stepwise motion electrostatic actuator made of doped polysilicon. Remote control is obtained by inductive coupling at 13.56 MHz thanks to a high-voltage IC specially dedicated to that purpose.Results
Each DMMS is composed of 1,700 actuators, presents a capacitance of 2 nF and a pull-in voltage of 20 V. The HV die makes it possible to power but also to remote control a double electrostatic Ciliary Motion System (CMS), allowing a two degrees of freedom displacement. Voltages up to 100 V can be used. The receiver antenna is a hollow coil made of electroplated gold on a flexible SU8 substrate. This was to prevent eddy currents and made the antenna as light as possible. The emitter system needs 9 W to fully actuate the DMMS at a distance of 1 cm. The maximum actuation frequency is 20 Hz.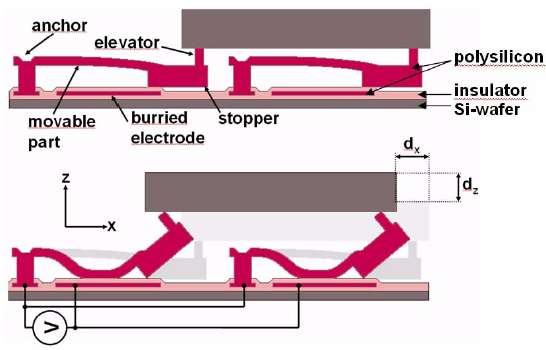
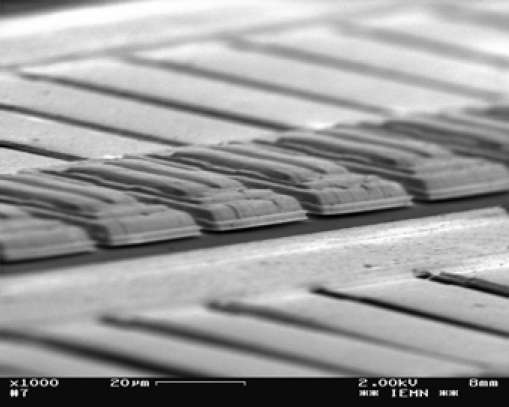
Principle and SEM picture of the actuators.

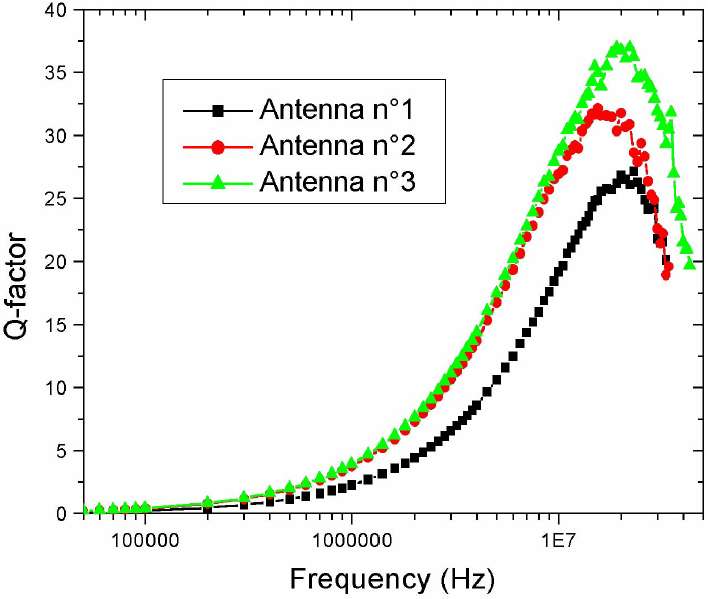
Picture and Q-factor of flexible receiver antennas.
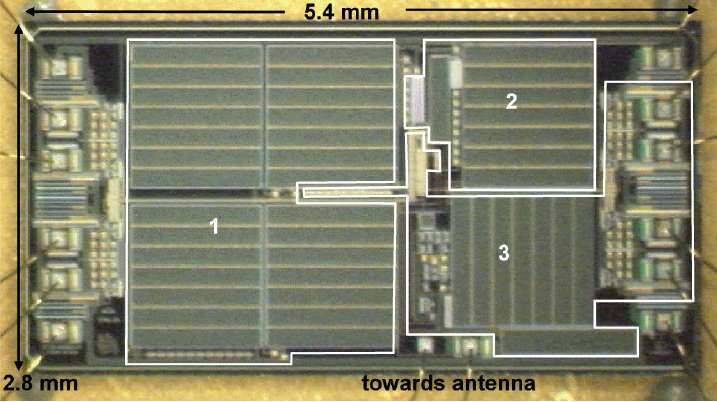
Microphotograph of the IC: 1- rectifier and limiter of the induced voltage,
2- clock recovery and and 5 V-regulator, 3- demodulator, digital processing and high-voltage output buffer.
Related publications
Journals
 "Complete
system for wireless powering and remote control
of MEMS
devices by inductive coupling", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, B.
Legrand, D.
Collard and L. Buchaillot, IEEE/ASME
Transactions
on Mechatronics, vol 12,
no 1, pp. 23-31, feb 2007
"Complete
system for wireless powering and remote control
of MEMS
devices by inductive coupling", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, B.
Legrand, D.
Collard and L. Buchaillot, IEEE/ASME
Transactions
on Mechatronics, vol 12,
no 1, pp. 23-31, feb 2007
 "Process and realization of
a 3D gold electroplated
antenna on a
flexible epoxy film for wireless micro-motion system", P.
Basset, A.
Kaiser, D. Collard and L. Buchaillot, Journal
of
Vacuum Science
Technology, Vol. B 20 (4), pp. 1465-1470,
Jul/Aug, 2002
"Process and realization of
a 3D gold electroplated
antenna on a
flexible epoxy film for wireless micro-motion system", P.
Basset, A.
Kaiser, D. Collard and L. Buchaillot, Journal
of
Vacuum Science
Technology, Vol. B 20 (4), pp. 1465-1470,
Jul/Aug, 2002
Book's chapter
- "Remote powering and control of intelligent microsystems", P. Basset, L. Buchaillot, A. Kaiser, Smart adaptive systems on silicon, Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 253-268, 2004
PhD dissertation (in French)
 "Design, fabrication and test
of a
wireless Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System (MEMS) for
micro-transport applications ", P. Basset,, PhD
dissertation,
june 2003
"Design, fabrication and test
of a
wireless Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System (MEMS) for
micro-transport applications ", P. Basset,, PhD
dissertation,
june 2003
Conferences
- "Remote
Actuation of Independent
Electrostatic Distributed Micromechanical Systems (DMMS) for a Wireless
Microrobot", P. Basset, L.
Buchaillot, D. Collard, A. Kaiser, Proceeding
of the Conference of the IEEE Industrial
Electronics Society (IECON’06),
Paris, France, 2006
 "A 100V IC for the remote
powering and independant
control of multiple
electrostatic actuators", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, B.
Stefanelli, M.
Wallenne, D. Collard and L. Buchaillot, Proceeding
of the 12th
int.
Conf. on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems
(Transducers’03),
Boston, USA., pp. 1711-1713, 2003
"A 100V IC for the remote
powering and independant
control of multiple
electrostatic actuators", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, B.
Stefanelli, M.
Wallenne, D. Collard and L. Buchaillot, Proceeding
of the 12th
int.
Conf. on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems
(Transducers’03),
Boston, USA., pp. 1711-1713, 2003
 "A large stepwise motion
electrostatic actuator for
wireless
microrobot", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, P. Bigotte, D. Collard and
L.
Buchaillot, Proceeding of the 15th IEEE Micro Electro
Mechanical System
(MEMS’02),
pp. 606-609, Las Vegas, U.S.A., 2002
"A large stepwise motion
electrostatic actuator for
wireless
microrobot", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, P. Bigotte, D. Collard and
L.
Buchaillot, Proceeding of the 15th IEEE Micro Electro
Mechanical System
(MEMS’02),
pp. 606-609, Las Vegas, U.S.A., 2002
- "Design of an autonomous microrobot", P. Basset, A. Kaiser, B. Stefanelli, D. Collard, L. Buchaillot, Proceeding of the 8th IEEE int. Conf. on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA’01), pp. 773-736, Antibes-Juan les Pins, France, Oct. 15-18, 2001
- "Electrostatic impact drive actuator", M. Mita, M. Arai, S. Tensaka, D. Kobayashi, P. Basset, A. Kaiser, P. Masquelier, L. Buchaillot, D. Collard and H. Fujita, Proc. 14th IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS’01), Interlaken, Switzerland, pp. 590-593, 2001
Maintained by Webmaster