Projet VibRoT (2014-2017)
"Low-frequency MEMS e-VEHs powered by human mouvement -
application to wireless sensors and RFID tags"
Grants : UPE / UPMC / SATT IdF Innov
Project Goals
Results
Publications
Project Goals
In the continuity of the NEHSTech project, we intended in VIBROT to optimize our low-frequency electrostatic Vibration Energy Harvesters (e-VEH) in order to power wireless sensors and RFID tags for the next generation of Internet and RFID of Things (I/RoT). Several features are added/improved:- to avoid having to bias the device with a dc source, electret is now implemented by corona charging of a vertical parylen layer,
- frequency-up conversion behavior is optimized to fit low-frequency applications,
- capacitance variation of the transducer is increased by improving the fabrication process and optimizing the electrode shapes.
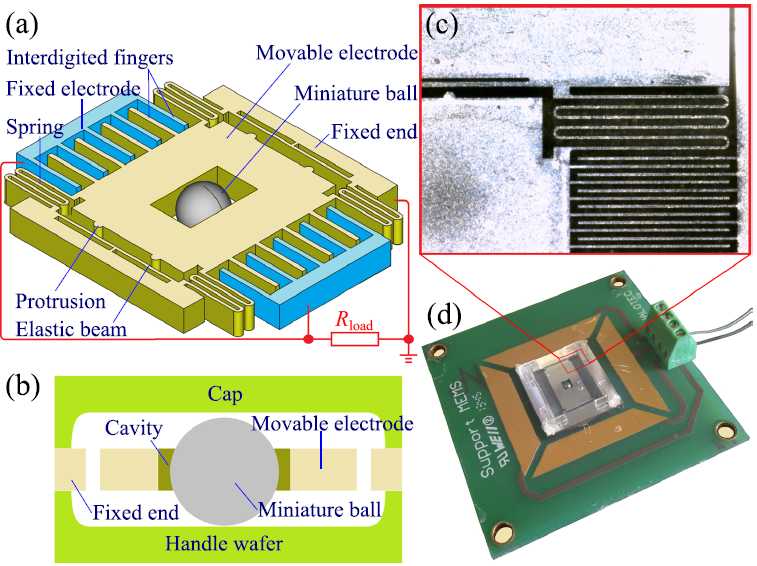
Schematic of the core structure (a) and the cross section of the full device (b);
Microscopic photograph of silicon structures (c) and optical photograph of the full device (d).
Results
2nd and 3rd generation of low-frequency e-VEHs : vertical electret and frequency-up conversion
With the 2nd generation of LF e-VEH, we have demonstrated the first corona charging of vertical electret and a double frequency-up conversion behavior, with elastic stoppers and/or with the additional milliball.With the 3rd generation, we included microstructuration of the electrodes in the gap-closing electrosatic actuator to drastically reduce the air damping. This allowed to reach an effectiveness of more than 50%.
We also powered a wireless sensor node with data transmission at 868 MHz and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocols.
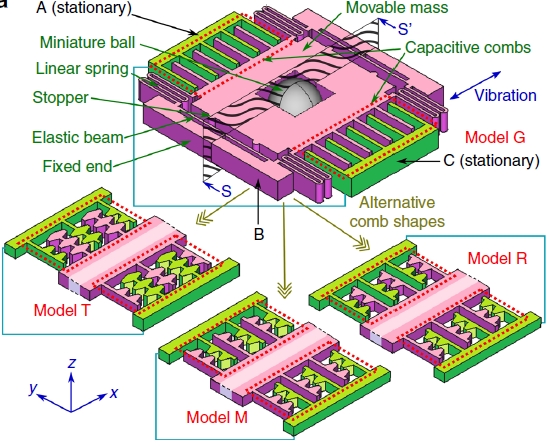
Different structures studied for decreasing the air damping. Best results are obtained with model R.
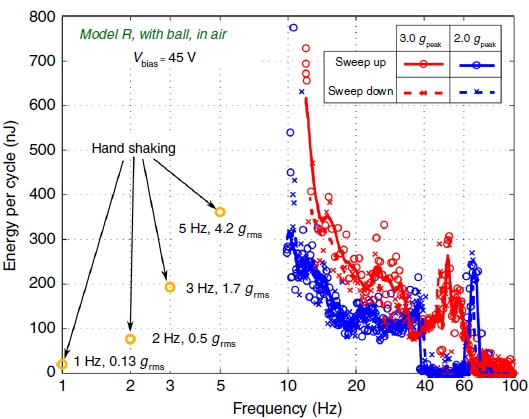
Energy conversion of Model R in air.
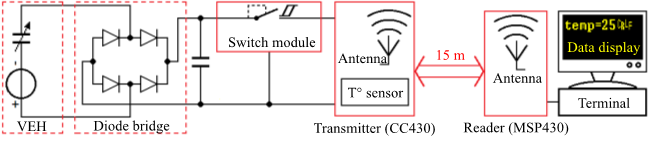
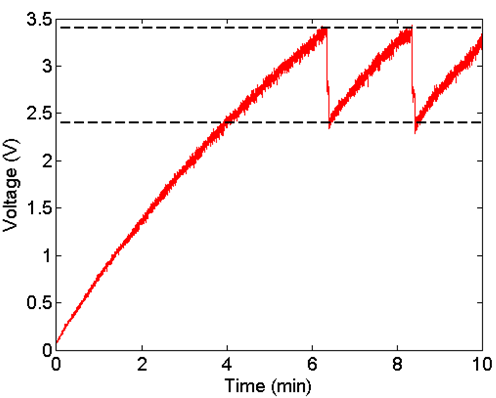
Experiment of data transmission with 2nd generation in air: Setup from CEA Leti and Voltage evolution on C at 3 grms / 100 Hz. (Initial charging time = 6.4 min. Following charging time = 2 min).
Related publications
Journals
 “An
impact-coupled MEMS electrostatic kinetic energy harvester and its
predictive model taking nonlinear air damping effect into account”,
Y. Lu, J. Juillard, F. Cottone, D. Galayko and P. Basset, IEEE Journal
of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 27, no 6, 1041-1053, 2018
“An
impact-coupled MEMS electrostatic kinetic energy harvester and its
predictive model taking nonlinear air damping effect into account”,
Y. Lu, J. Juillard, F. Cottone, D. Galayko and P. Basset, IEEE Journal
of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 27, no 6, 1041-1053, 2018
 “A power supply
module for autonomous portable electronics: ultralow-frequency MEMS
electrostatic kinetic energy harvester with hierarchical comb structure
reducing air damping”,
Y. Lu , F. Marty, D. Galayko, J.-M. Laheurte and P. Basset, IECAS/NPG
Microsystems and Nanoengineering, vol.4, no 28, pp. 1041-1053, 2018
“A power supply
module for autonomous portable electronics: ultralow-frequency MEMS
electrostatic kinetic energy harvester with hierarchical comb structure
reducing air damping”,
Y. Lu , F. Marty, D. Galayko, J.-M. Laheurte and P. Basset, IECAS/NPG
Microsystems and Nanoengineering, vol.4, no 28, pp. 1041-1053, 2018
 "Performance Evaluation of a Long-Range
RFID Tag Powered by a Vibration Energy Harvester", Y.
Lu, P. Basset and J.M. Laheurte, , IEEE Antennas and
Wireless Propagation Letter, vol. 16, pp.
1832 – 1835, 2017
"Performance Evaluation of a Long-Range
RFID Tag Powered by a Vibration Energy Harvester", Y.
Lu, P. Basset and J.M. Laheurte, , IEEE Antennas and
Wireless Propagation Letter, vol. 16, pp.
1832 – 1835, 2017
 “A batch-fabricated electret-biased wideband MEMS vibration
energy harvester with frequency-up conversion behavior powering a UHF wireless
sensor node”, Y. Lu, E. O’Riordan, F. Cottone, S.
Boisseau, D. Galayko, E. Blokhina, F. Marty, and P. Basset , IOP Journal of Micromechanics and
Microengineering, Vol. 26, no 12, 2016
“A batch-fabricated electret-biased wideband MEMS vibration
energy harvester with frequency-up conversion behavior powering a UHF wireless
sensor node”, Y. Lu, E. O’Riordan, F. Cottone, S.
Boisseau, D. Galayko, E. Blokhina, F. Marty, and P. Basset , IOP Journal of Micromechanics and
Microengineering, Vol. 26, no 12, 2016
 “A Nonlinear MEMS Electrostatic Kinetic Energy
Harvester for Human-Powered Biomedical Devices”, Y. Lu, F. Cottone, S. Boisseau,
F. Marty, D. Galayko and P. Basset, AIP Applied
Physics Letters, 107, 253902 (2015)
“A Nonlinear MEMS Electrostatic Kinetic Energy
Harvester for Human-Powered Biomedical Devices”, Y. Lu, F. Cottone, S. Boisseau,
F. Marty, D. Galayko and P. Basset, AIP Applied
Physics Letters, 107, 253902 (2015)
Conferences
- “New comb geometry of capacitive vibration energy harvesters miniaturizing the air damping effect”, Y. Lu, F. Marty, D. Galayko and P. Basset, Proc. of the 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS’17), Las Vegas, USA, 2017 - Nominated for best paper
 “MEMS
electrostatic vibration energy harvester with
ultra-wide and low frequency bandwidth powering an autonomous
temperature wireless sensor node”, Y. Lu, F. Cottone, S. Boisseau, D. Galayko, F.
Marty and P. Basset, Proc.
of the 29th Int. Conf. on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS’16),
Shanghai, China, 2016
“MEMS
electrostatic vibration energy harvester with
ultra-wide and low frequency bandwidth powering an autonomous
temperature wireless sensor node”, Y. Lu, F. Cottone, S. Boisseau, D. Galayko, F.
Marty and P. Basset, Proc.
of the 29th Int. Conf. on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS’16),
Shanghai, China, 2016
Maintained by Webmaster
