grayscale homotopic thinning More...
Detailed Description
grayscale homotopic thinning
Usage: hthin in.pgm {imcond.pgm|null} connex niter out.pgm
Description: Grayscale homotopic thinning (refs. [BEC97, CBB01]). The parameter connex gives the connectivity used for the minima; possible choices are 4, 8 in 2D and 6, 26 in 3D. Let F be the function corresponding to the input image in.pgm. Let G be the function corresponding to the input image imcond.pgm, or the null function if the keyword null is used. The algorithm is the following:
Repeat niter times:
L = {(p,d) such that p is destructible for F and d = delta-(p,F)}
While L not empty
extract a couple (p,d) from L
F(p) = max{ d, delta-(p,F), G(p) }
Result: F
If niter is set to -1, then the operator iterates until stability.
References:
[BEC97] G. Bertrand, J. C. Everat and M. Couprie: "Image segmentation through operators based upon topology", Journal of Electronic Imaging, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 395-405, 1997.
[CBB01] M. Couprie, F.N. Bezerra, Gilles Bertrand: "Topological operators for grayscale image processing", Journal of Electronic Imaging, Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 1003-1015, 2001.
Types supported: byte 2D, byte 3D.
Category: topogray
Example:
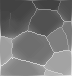
hthin ur1 null 4 10 ur1_hthin
minima ur1_hthin 4 ur1_hthin_m

| 
| 
|
| ur1 | ur1_hthin | ur1_hthin_m |
 1.7.3
1.7.3