ultimate binary skeleton guided by a priority image (see [BC07]) More...
Detailed Description
ultimate binary skeleton guided by a priority image (see [BC07])
Usage: skeleton in.pgm prio connex [inhibit] out.pgm
Description: Ultimate binary skeleton guided by a priority image. The lowest values of the priority image correspond to the highest priority.
The parameter prio is either an image (byte, int32_t, float or double), or a numerical code indicating that a distance map will be used as a priority image; the possible choices are:
- 0: approximate euclidean distance
- 1: approximate quadratic euclidean distance
- 2: chamfer distance
- 3: exact quadratic euclidean distance
- 4: 4-distance in 2d
- 8: 8-distance in 2d
- 6: 6-distance in 3d
- 18: 18-distance in 3d
- 26: 26-distance in 3d
The parameter connex indicates the connectivity of the binary object. Possible choices are 4, 8 in 2d and 6, 26 in 3d.
If the parameter inhibit is given and is an integer different from -1, then the points which correspond to this priority value will be left unchanged. If the parameter inhibit is given and is a binary image name, then the points of this image will be left unchanged.
Let X be the set corresponding to the input image in.pgm. Let P be the function corresponding to the priority image. Let I be the set corresponding to the inhibit image, if given, or the empty set otherwise. The algorithm is the following:
Repeat until stability
Select a point x in X \ I such that P[x] is minimal
If x is simple for X then
X = X \ {x}
Result: X
Reference:
[BC07] G. Bertrand and M. Couprie: "Transformations topologiques discretes", in Géométrie discrète et images numériques, D. Coeurjolly and A. Montanvert and J.M. Chassery, pp. 187-209, Hermès, 2007.
Types supported: byte 2d, byte 3d
Category: topobin
Example:
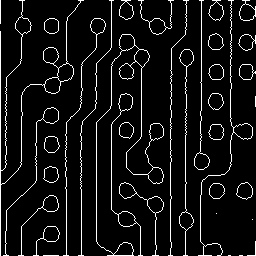
skeleton circuit1 8 8 circuit1_skeleton
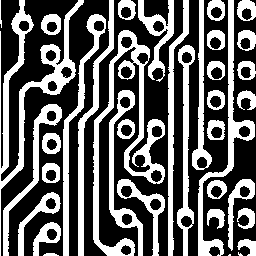
| 
|
| circuit1 | circuit1_skeleton |
 1.7.3
1.7.3