5.4.8. L2-ball#
For a given scalar \(\xi \ge 0\), the L2-ball is a convex constraint defined as
where \(\|{\bf w}\|_2 = \sqrt{w_1^2+\dots+w_N^2}\) is the L2-norm. The condition \(\xi \ge 0\) is required for this subset to be nonempty. The figure below shows how this constraint looks like in \(\mathbb{R}^{2}\) or in \(\mathbb{R}^{3}\).
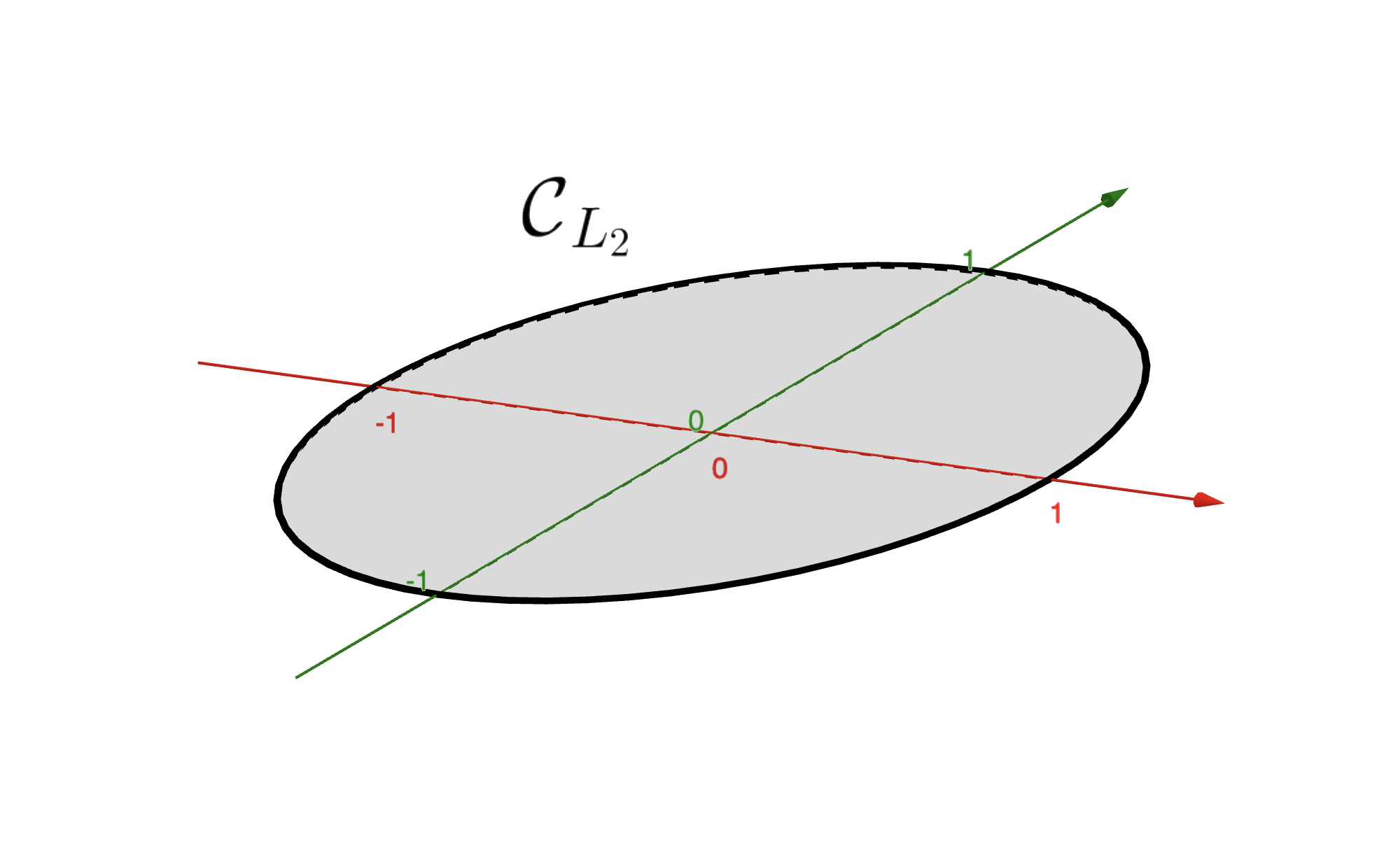
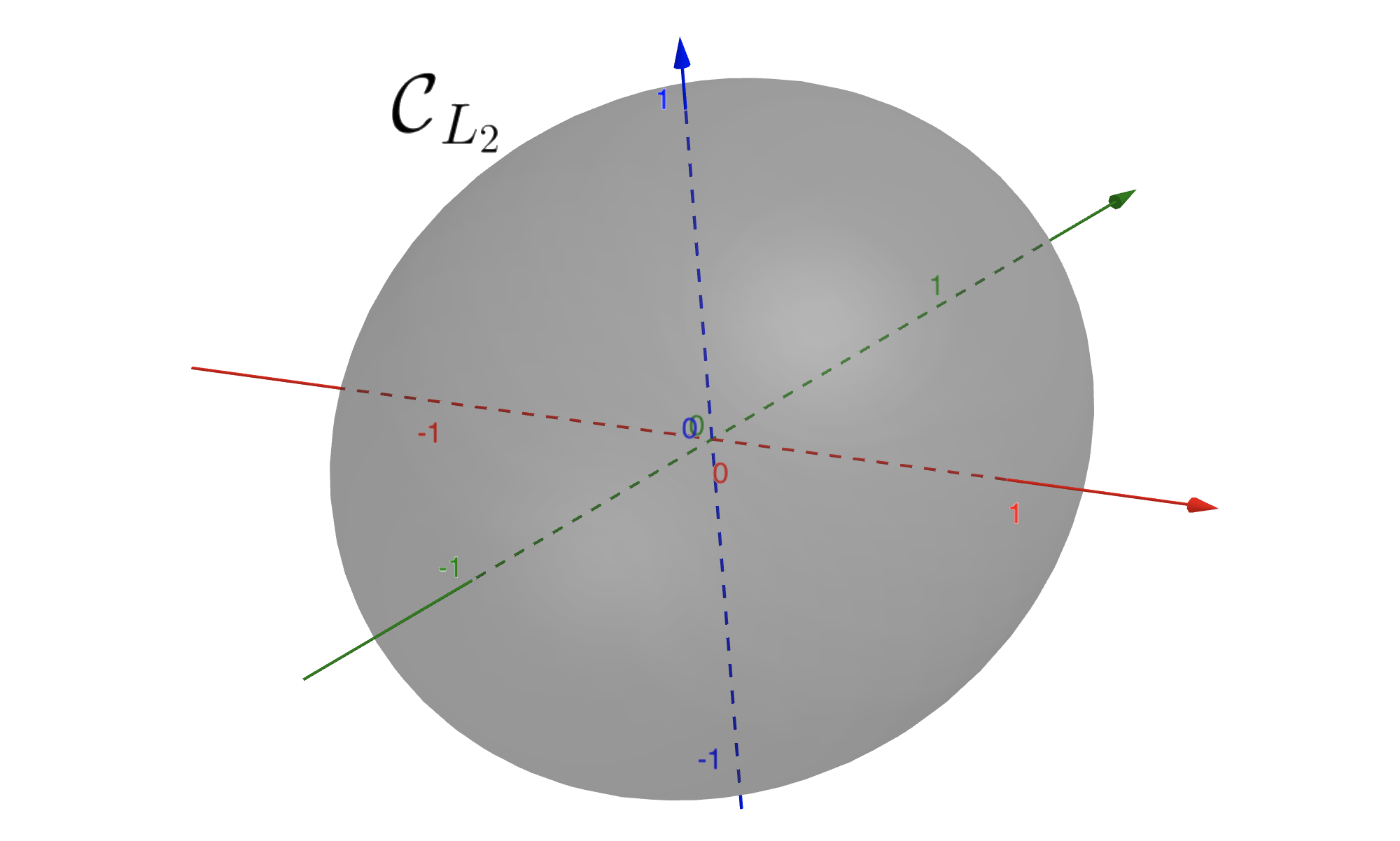
5.4.8.1. Constrained optimization#
Optimizing a function \(J({\bf w})\) subject to the L2-ball constraint can be expressed as
The figure below visualizes such an optimization problem in \(\mathbb{R}^{2}\).
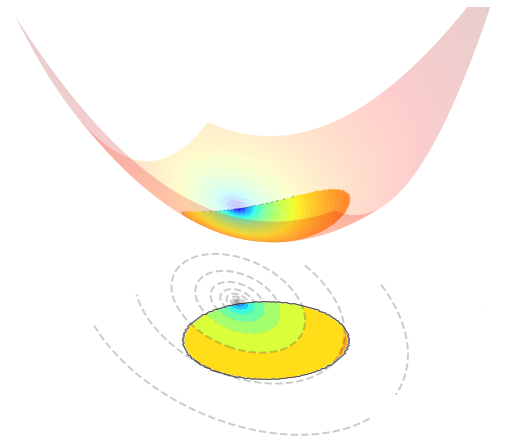
5.4.8.2. Orthogonal projection#
The projection of a point \({\bf u}\in\mathbb{R}^{N}\) onto the L2-ball is the (unique) solution to the following problem
The solution can be analytically computed as follows.
Projection onto the L2-ball
The next figure visualizes a point \({\bf u}\in \mathbb{R}^{2}\) (blue dot) along with its projection (red dot) onto this set.
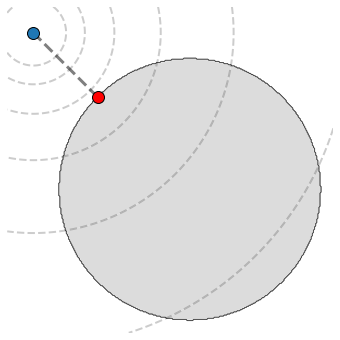
5.4.8.3. Implementation#
The python implementation is given below.
def project_l2ball(u, bound):
assert bound >= 0, "The bound must be non-negative"
if np.linalg.norm(u) < 1e-16:
p = np.zeros(u.shape)
else:
p = u * np.minimum(1, bound / np.linalg.norm(u))
return p
Here is an example of use.
u = np.array([-1.2, 1.2])
p = project_l2ball(u, bound=1)
